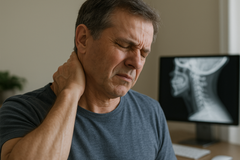
A herniated disc, commonly referred to as a slipped disc, prolapsed intervertebral disc, or disc herniation, is a condition that affects the spine. It occurs when a part of the intervertebral disc, specifically the nucleus pulposus, protrudes through a tear in the surrounding annulus fibrosus. This protrusion can exert pressure on nearby nerves, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness in the back and extremities. Understanding this condition is crucial, especially for individuals who experience chronic back pain or work in physically demanding jobs that put significant strain on the back.
A herniated disc, commonly referred to as a slipped disc, prolapsed intervertebral disc, or disc herniation, is a condition that affects the spine. It occurs when a part of the intervertebral disc, specifically the nucleus pulposus, protrudes through a tear in the surrounding annulus fibrosus. This protrusion can exert pressure on nearby nerves, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness in the back and extremities. Understanding this condition is crucial, especially for individuals who experience chronic back pain or work in physically demanding jobs that put significant strain on the back.
the importance of understanding herniated discs
Back pain is one of the most common reasons people seek medical attention, and a herniated disc is often a key culprit. For those working in occupations that involve heavy lifting, repetitive motions, or prolonged sitting, the risk of developing a herniated disc increases. Recognizing the symptoms early and understanding the condition can lead to more effective management and treatment, potentially preventing long-term discomfort or disability.
The significance of this topic extends beyond those currently suffering from back pain. With the modern lifestyle increasingly characterized by sedentary behavior and poor ergonomics, the prevalence of spinal issues is on the rise. By educating oneself about the causes and symptoms of a herniated disc, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their spinal health, whether through lifestyle adjustments, ergonomic improvements, or seeking timely medical advice.
what to expect from this guide
This blog post aims to provide a comprehensive overview of herniated discs, offering insights into the anatomy of the spine, the causes of disc herniation, and the variety of symptoms one might experience. We will explore the diagnostic processes that healthcare professionals use to confirm a herniated disc, including physical examinations and advanced imaging techniques such as MRI and CT scans.
Moreover, we will delve into the treatment options available, ranging from conservative approaches like physical therapy and medication to more invasive procedures like surgery. Innovative treatments and technologies that aid recovery will also be discussed, alongside how ergonomic tools from Anodyne can support individuals in managing their condition.
By the end of this guide, readers will have a clearer understanding of herniated discs, empowering them to make informed decisions about their health and treatment options. Whether you're dealing with back pain yourself or seeking to prevent future issues, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of spinal health.
anatomy and causes of a herniated disc
The spine is a complex structure composed of vertebrae, intervertebral discs, nerves, and supporting muscles and ligaments. These intervertebral discs act as cushions between the vertebrae, allowing for flexibility and absorbing shock during movement. Each disc consists of a tough outer layer called the annulus fibrosus and a gel-like center known as the nucleus pulposus. A herniated disc occurs when the nucleus pulposus pushes through a tear in the annulus fibrosus, potentially pressing on nearby nerves and causing pain and discomfort.
Several factors contribute to the development of a herniated disc. Age-related degeneration is a common cause, as the discs lose hydration and elasticity over time, making them more prone to tears. Physical trauma, such as a fall or accident, can also lead to disc herniation. Additionally, lifestyle factors like poor posture, improper lifting techniques, and repetitive stress on the spine can increase the risk of a herniated disc. Understanding these causes is crucial for both prevention and effective management of the condition.
symptoms and diagnosis of a herniated disc
Recognizing the symptoms of a herniated disc is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include localized back pain, which may radiate to the arms or legs if the herniation affects the cervical or lumbar spine. Patients might also experience numbness, tingling, or weakness in the extremities, depending on the affected nerves. In severe cases, loss of bowel or bladder control can occur, indicating a medical emergency.
Diagnosing a herniated disc typically involves a comprehensive physical examination by a healthcare professional, who will evaluate the patient's medical history and symptoms. Imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans are often employed to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the herniation. These tools provide detailed images of the spine, helping to pinpoint the exact location and severity of the disc herniation.
treatment options for herniated discs
There are various treatment options available for managing a herniated disc, ranging from conservative approaches to surgical interventions. Conservative treatments are usually the first line of defense and may include physical therapy, which focuses on strengthening the muscles supporting the spine and improving flexibility. Pain management through medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroid injections can also provide relief.
In cases where conservative treatments fail to alleviate symptoms or if the herniation is severe, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options include discectomy, where the protruding portion of the disc is removed, or spinal fusion, which stabilizes the affected vertebrae. Recent advances in minimally invasive surgery have improved recovery times and outcomes for patients undergoing these procedures.
Innovative technologies and ergonomic tools, like those offered by Anodyne, can play a significant role in supporting individuals with a herniated disc. Ergonomic solutions, such as adjustable chairs and supportive cushions, help maintain proper posture and reduce strain on the spine, contributing to both recovery and prevention of future disc issues.

Lendengurt
Stützt und stabilisiert den unteren Rücken – individuell anpassbar für Alltag und Arbeit.
In conclusion, understanding the anatomy, causes, and treatment options for a herniated disc is vital for effective management and recovery. By recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate medical advice, individuals can explore a range of treatments to alleviate pain and improve their quality of life. With the right approach, including lifestyle adjustments and ergonomic improvements, many people can successfully manage a herniated disc and maintain a healthy spine.
recovery and prevention of a herniated disc
Recovering from a herniated disc requires a multifaceted approach that includes rest, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments. Initially, it's crucial to allow the affected area to heal by avoiding activities that exacerbate pain. Gradually, incorporating exercises designed to strengthen the core muscles can aid in stabilizing the spine and preventing future injuries. These exercises often focus on improving flexibility, strength, and posture, which are essential for maintaining spinal health.

Women's Posture Shirt™ - Schwarz
Patentiertes Shirt zur Verbesserung der Körperhaltung und Linderung von Rückenbeschwerden.
Lifestyle changes play a significant role in both recovery and prevention. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the strain on the spine, while regular physical activity helps keep the back muscles strong and flexible. Ergonomic adjustments at work and home, such as using supportive chairs and desks, can also minimize the risk of re-injury. Additionally, practicing proper lifting techniques and avoiding prolonged sitting or standing can significantly reduce the likelihood of experiencing another herniated disc.
case studies and patient experiences
Real-life experiences from individuals who have successfully managed a herniated disc can provide valuable insights and encouragement. Consider the case of John, a 45-year-old office worker who suffered from severe back pain due to a herniated disc. Through a combination of physical therapy, ergonomic adjustments at his workstation, and a tailored exercise regimen, John was able to regain his mobility and return to his daily activities without pain. His story highlights the importance of a comprehensive approach to treatment and the positive impact of proactive measures.
Similarly, Sarah, a 32-year-old nurse, experienced a herniated disc from repetitive lifting at work. After undergoing physical therapy and learning proper body mechanics, she not only recovered but also implemented preventative strategies to protect her spine. These stories underscore the effectiveness of individualized treatment plans and the potential for a full recovery with the right support and guidance.
häufig gestellte fragen
what is the difference between a herniated disc and a bulging disc?
A herniated disc occurs when the inner gel-like nucleus pulposus breaks through the outer layer of the disc, while a bulging disc involves the disc protruding outward but remaining intact. Herniated discs are typically more severe and may cause more pronounced symptoms due to nerve compression.
how long does recovery from a herniated disc take?
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the herniation and the treatment approach. Many people experience relief within a few weeks to a few months with conservative treatment, while others may require longer or surgical intervention for full recovery.
can a herniated disc heal without surgery?
Yes, many herniated discs heal with non-surgical treatments such as physical therapy, pain management, and lifestyle modifications. Surgery is typically considered when conservative treatments fail to provide relief or if there are significant neurological deficits.
what exercises are helpful for a herniated disc?
Exercises that focus on strengthening the core, improving flexibility, and enhancing posture are beneficial. Activities like gentle stretching, yoga, and pilates can support recovery. It's essential to consult with a physical therapist to ensure exercises are performed safely and effectively.
how can I make my workplace more ergonomic to avoid back pain?
Improving workplace ergonomics involves adjusting your chair and desk to ensure proper posture, using supportive cushions, and positioning your computer monitor at eye level. Regular breaks to stand and stretch can also help reduce strain on the spine.
Understanding and addressing a herniated disc through informed decisions and proactive measures can lead to effective management and prevention. By adopting a holistic approach that includes treatment, lifestyle changes, and ergonomic improvements, individuals can enhance their spinal health and overall well-being.
Källor
- Wikipedia. "Disc Herniation."
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. "Herniated Disk."
- Mayo Clinic. "Herniated Disk: Symptoms and Causes."
- StatPearls. "Herniated Disc."
- University Hospital Zurich. "Herniated Disc."
- UC Davis Health. "Disc Herniation."
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. "Herniated Disk in the Lower Back."
- American Association of Neurological Surgeons. "Herniated Disc."
- Bab.la. "Bandscheibenvorfall: German-English Dictionary."
- Harvard Health. "Herniated Disk A to Z."
- OrthoZentrum Freiburg. "Bandscheibenvorfall."
- Mayo Clinic. "Herniated Disk: Diagnosis and Treatment."
- Leading Medicine Guide. "Herniated Disk."
- Cleveland Clinic. "Herniated Disk."
- MedlinePlus. "Herniated Disk."